The maximum score on each section of the test is 30 points. The maximum score for the test is 120 points.
Scores are valid for 2 years. If a person takes the test more than one time, then the person can keep the highest score on each section (My Best Score). For example, if on the first test, the person gets 21 points on the reading section, but on the second test, the person gets 18 points on the reading section, then the person can keep the 21 points on the reading section and use it as part of his or her official score.
1. Reading Section
On the reading section, scores are determined based on the number of correct answer choices to questions. The number of correct answers is used to create a “raw score”. This score is higher than 30 points, and it is based on the number of points that are possible from the questions in the section. It is possible for a question to have a value of more than 1 point. The “raw score” is then turned into a “scaled score”. This score depends on the difficulty of the section and is adjusted by ETS on a test-by-test basis. The “scaled score” is the official score that a person gets for the reading section. Here is a sample of a scoring chart:
*Raw Score: Scaled Score
2. Listening Section
On the listening section, scores are determined based on the number of correct answer choices to questions. The number of correct answers is used to create a “raw score”. This score is lower than 30 points, and it is based on the number of points that are possible from the questions in the section. It is possible for a question to have a value of more than 1 point. The “raw score” is then turned into a “scaled score”. This score depends on the difficulty of the section and is adjusted by ETS on a test-by-test basis. The “scaled score” is the official score that a person gets for the listening section. Here is a sample of a scoring chart: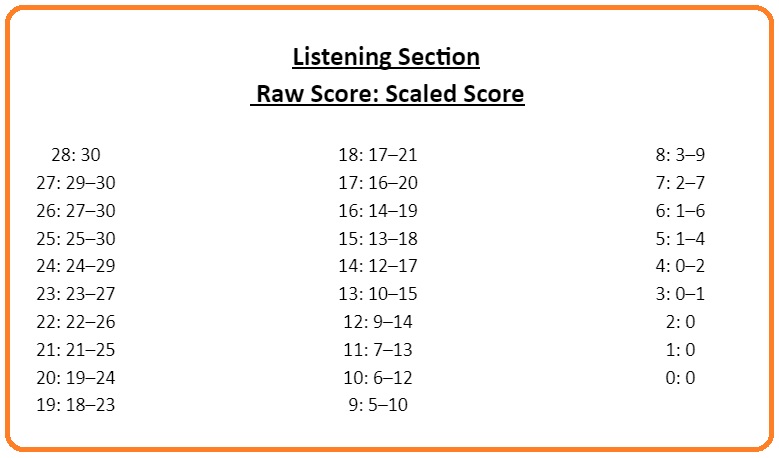
*Raw Score: Scaled Score
3. Speaking Section
On the speaking section, responses are sent to ETS for evaluation. Scores are based on human evaluators and an AI evaluation program.
There are 4 exercises, and each of them is scored from 0 to 4 points by a human evaluator and the AI evaluation program. These scores are whole numbers. From these 8 scores, an average is calculated, and this average is multiplied by a conversion rate of 7.5 to determine a person’s score on the speaking section. Here is a sample of student score:
Speaking 1: Human Evaluator [3] / AI Evaluator [3]
Speaking 2: Human Evaluator [2] / AI Evaluator [3]
Speaking 3: Human Evaluator [3] / AI Evaluator [2]
Speaking 4: Human Evaluator [3] / AI Evaluator [2]
Average Score: 2.625
Average Score x Conversion Rate = 19.675 -> 20 points
Scores are determined by various measures. Here is a general description:
A person who speaks well is easy to understand, does not pause much while speaking, speaks at a natural speed and rhythm, has good pronunciation, and has appropriate intonation based on the specific intonation.
A person who speaks well can use a variety of grammar structures in a natural way, uses a variety of vocabulary in a natural way, uses the appropriate words and grammar based on the specific situation, and makes few mistakes with grammar and word choice. If there are some mistakes, they do not affect the ability to understand what is said.
A person who speaks well shows a clear understanding of the question or the material related to the question, answers the question well with relevant details and examples, provides relevant and accurate information from the material related to the question, and organizes information in a format that is easy to understand and appropriate to the task.
The official scoring procedure of the speaking section is not made public by ETS. The above information is based on the best estimate that can be made by MLI based on available information and student performance.
4. Writing Section
On the writing section, responses are sent to ETS for evaluation. Scores are based on human evaluators and an AI evaluation program. There are 2 exercises, and each of them is scored from 0 to 5 points by a human evaluator and the AI evaluation program. These scores are whole numbers. From these 4 scores, an average is calculated, and this average is multiplied by a conversion rate of 6 to determine a person’s score on the speaking section. Here is a sample of student score:
Writing 1: Human Evaluator [3] / AI Evaluator [4]
Writing 2: Human Evaluator [3] / AI Evaluator [2]
Average Score: 3
Average Score x Conversion Rate = 18 -> 18 points
Scores are determined by various measures. Here is a general description:
A person that writes well is able to choose important information from the listening portion of the exercise, explain it in an understandable and accurate way, and connect it to relevant information in the reading portion of the exercise. The writing is organized in a format that is appropriate to the task and has few mistakes in grammar and spelling. If there are some mistakes, they do not affect the ability to understand what is written.
A person that writes well has ideas, reasons, and examples that are clear, developed, and include relevant details. The writing is organized in a format that is easy to understand and the purpose of each paragraph is clear and meaningful to the question. The writing is not repetitive and does not include unrelated information.
The writing includes a variety of grammar structures, has a variety of vocabulary, contains the appropriate words and grammar based on the specific situation, and makes few mistakes with grammar and spelling. If there are some mistakes, they do not affect the ability to understand what is written. The writing also includes grammar and vocabulary that are formal and advanced.
The official scoring procedure of the writing section is not made public by ETS. The above information is based on the best estimate that can be made by MLI based on available information and student performance.
Lastly, the TOEFL iBT uses a different scoring system than other English proficiency tests. In order to understand how a TOEFL iBT score compares to scores on the IELTS and TOEIC tests, please refer to the chart below.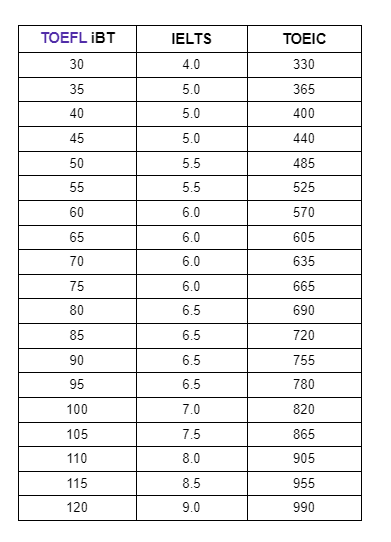
Kyle Hanano has been an English teacher since 2005. He has experience teaching students of all ages and skill levels. However, he has the most teaching experience in test preparation, especially in regards to the TOEFL examination. He has been a part of Mentor Language Institute since 2008. Prior to that, he was an assistant language teacher in Japan with the JET Programme for three years. He holds a B.A. in English Literature and a B.A. in Japanese Language and Culture from the University of California at Los Angeles, and he graduated in 2005.








